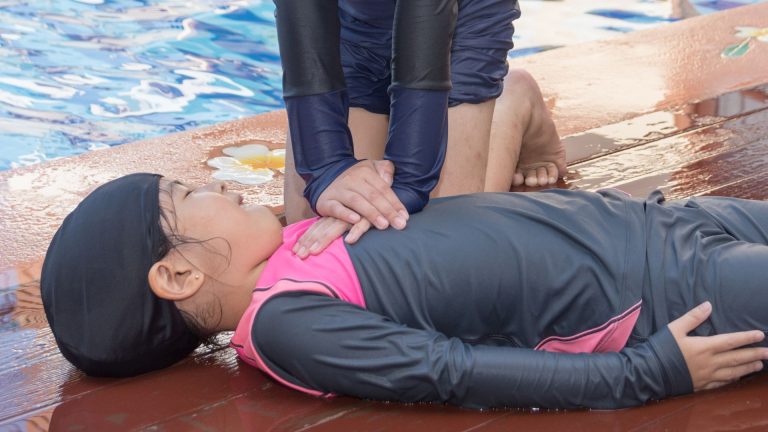
Drowning is a critical emergency that requires immediate and effective intervention. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a lifesaving technique used in such situations, but water rescues present unique challenges that differentiate them from other emergencies. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone involved in water safety, from lifeguards to bystanders. This article explores the specific aspects of CPR for drowning victims, highlighting the importance of timely intervention, the role of rescue breathing, and the environmental factors that influence the rescue process.
THE IMPORTANCE OF TIMELY INTERVENTION
In drowning situations, time is of the essence. The brain can suffer irreversible damage after just four to six minutes without oxygen. Therefore, the speed at which a victim is rescued and CPR is initiated can significantly impact the outcome. Unlike other emergencies where CPR might be performed immediately, water rescues often involve additional steps before CPR can begin. The victim must first be safely removed from the water, which can be complicated by factors such as water currents, the victim’s location, and the rescuer’s ability to reach them. Once the victim is on land, CPR should be started without delay. The initial focus should be on providing rescue breaths, as drowning primarily causes respiratory arrest. This differs from other cardiac emergencies where chest compressions are prioritized. The goal is to restore breathing and circulation as quickly as possible to prevent brain damage and increase the chances of survival.
THE ROLE OF RESCUE BREATHING
Rescue breathing is a critical component of CPR for drowning victims. In most cardiac emergencies, chest compressions are emphasized to maintain circulation. However, in drowning cases, the primary issue is a lack of oxygen due to water inhalation. Therefore, rescue breaths are essential to provide the oxygen the victim’s body desperately needs. The process involves tilting the victim’s head back to open the airway, pinching the nose shut, and delivering two breaths into the mouth. Each breath should last about one second, ensuring the chest rises with each breath. This technique helps to expel water from the lungs and introduce fresh air, which is vital for reviving the victim. After delivering rescue breaths, chest compressions should be performed to support circulation. The combination of rescue breathing and chest compressions is crucial in addressing both respiratory and cardiac arrest, which are common in drowning incidents.
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS IN WATER RESCUES
Water rescues are inherently more complex due to various environmental factors. The location of the drowning incident, whether in a pool, lake, or ocean, can significantly affect the rescue process. In open water, currents, waves, and visibility can pose challenges for rescuers. Additionally, the temperature of the water can impact both the victim and the rescuer. Cold water can lead to hypothermia, which complicates the victim’s condition and may affect the rescuer’s ability to perform CPR effectively. Safety is a paramount concern during water rescues. Rescuers must assess the situation carefully to avoid putting themselves in danger. Using flotation devices can aid in safely bringing the victim to shore. Once on land, the rescuer must quickly transition to performing CPR, taking into account any additional complications such as water in the lungs or hypothermia. Understanding these environmental factors is essential for effective water rescues and successful CPR administration.
TRAINING AND PREPAREDNESS
Proper training and preparedness are vital for anyone involved in water activities. Lifeguards, swimming instructors, and even regular swimmers should be equipped with the knowledge and skills to perform CPR on drowning victims. Training programs often emphasize the unique aspects of water rescues, including the importance of rescue breathing and the challenges posed by different water environments. Regular practice and drills can help individuals maintain their skills and confidence in emergency situations. Additionally, having the right equipment, such as rescue tubes and automated external defibrillators (AEDs), can enhance the effectiveness of a rescue. Preparedness also involves understanding the local water conditions and potential hazards, which can help prevent drowning incidents from occurring in the first place. By being well-trained and prepared, individuals can make a significant difference in the outcome of drowning emergencies.
In conclusion, CPR for drowning victims involves specific techniques and considerations that set it apart from other emergency situations. The emphasis on timely intervention, the critical role of rescue breathing, and the influence of environmental factors all contribute to the complexity of water rescues. Proper training and preparedness are essential for anyone involved in water activities, ensuring they are equipped to handle these challenging situations effectively. By understanding and addressing the unique aspects of CPR for drowning victims, we can improve survival rates and outcomes in these life-threatening emergencies. For those interested in learning more about CPR and water safety, oakville first aid offers comprehensive training programs.